
Competitive Forces Model
Understand the six competitive forces
What is the Competitive Forces Model?
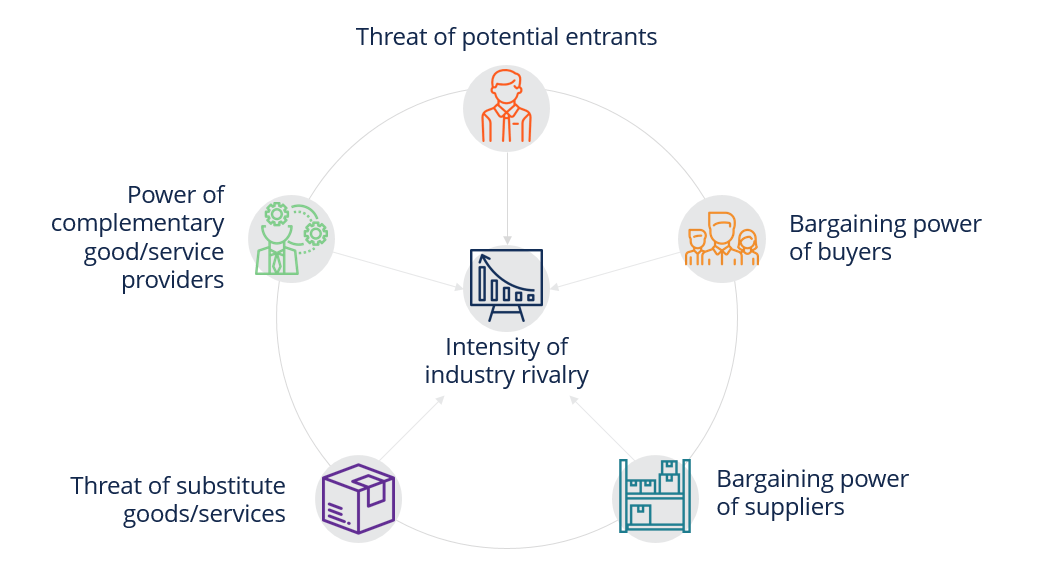
The Competitive Forces Model is an important tool used in strategic analysis to analyze the competitiveness in an industry. The model is more commonly referred to as the Porter’s Five Forces Model, which includes the following five forces: intensity of rivalry, threat of potential new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, and threat of substitute goods and/or services.
In our competitive forces model, we include a sixth force, the power of complementary goods and/or services providers. The model helps a company understand the risks in the industry it is operating in and decide how it wants to execute its strategies in response to competition.
Download the Free Template
Intensity of Industry Rivalry
There are multiple factors that can impact the intensity of rivalry within an industry.
- Concentration of rivals – the more competitors, the more intense the rivalry
- Product homogeneity – industries selling very similar products are likely to be more competitive
- Consumer switching costs – if it costs consumers a lot to switch from one company’s product to a competitor’s, the company is likely to face less competition
- Excess production capacity – when there is excess production capacity available in an industry, there is a higher chance of increased rivalry as companies find the industry more attractive to enter
- Brand loyalty – rivalry is high when customers have low brand loyalty
- Network effects – refers to the positive effect on the value of a product when there is an additional user of the product. When a network effect exists, the value of a product or service increases as more people are using it.
Threat of Potential Entrants
The threat of potential entrants is impacted by things such as:
- Brand loyalty
- Cost advantage or economies of scale – The threat of potential entrants tends to be higher when companies can realize economies of scale by mass production
- Switching costs
- Network effects
- Excess production capacity
- Government regulation – industries with strict government regulation pose a higher barrier to potential new entrants
- Barriers to exit – when exiting an industry requires high costs, companies are less likely to enter the industry in the first place
- Investment in specialist equipment – companies also consider the amount of capital that needs to be invested in specialist equipment when entering an industry
- High fixed costs – things such as specialist equipment, properties, and land are examples of high fixed costs
- Specialized skills – when entering an industry requiring specialized skills or techniques, there is a higher barrier to entry for potential entrants
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers is high when:
- Buyers are large or concentrated, so their decisions to purchase a product/service have bigger impacts on the company
- Buyers purchase a large percentage of volume
- Buyers have good information about the product, such as product pricing and demand
Buyers are price-sensitive when:
- There are many industry competitors, giving the buyers more choices with lower prices and better product attributes
- There are many substitutes available
- Switching costs are low, so buyers are indifferent between purchasing products from a company or its rivals
- Product homogeneity is high
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is high when:
- Suppliers are large or concentrated
- Suppliers can credibly threaten forward integration in the industry
- Rivals purchase a small percentage of the suppliers’ products
Purchasers’ price elasticity is high when:
- There are few alternative suppliers available
- There are few substitute inputs available
- Switching costs are high for purchasers
Threat of Substitute Goods/Services
Companies are likely to experience a high threat of substitute goods/services when:
- Switching costs are low for customers
- Substitutes have superior pricing relative to the current products
- Substitutes have better attributes or performance characteristics
Power of Complementary Good/Service Providers
Complementary goods or services can add value to the existing products in an industry. However, when complements have unattractive features or do not provide any value to consumers, they can actually become an issue for the industry by slowing growth and limiting profitability.
When developing strategies for a business, decision-makers should consider how they can potentially encourage complement providers to integrate and become a part of the business. Successful integration with complement providers is likely to expand market opportunities and bring profit-enhancing benefits to the business.
More Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to the Competitive Forces Model. Additional relevant CFI resources include:
