
Market Positioning
Influencing consumer perception of a brand or product in relation to rival brands
What is Market Positioning?
Market Positioning refers to the ability to influence consumer perception regarding a brand or product relative to competitors. The objective of market positioning is to establish the image or identity of a brand or product so that consumers perceive it in a certain way.
For example:
- A handbag maker may position itself as a luxury status symbol
- A TV maker may position its TV as the most innovative and cutting-edge
- A fast-food restaurant chain may position itself as the provider of cheap meals
Types of Positioning Strategies
There are several types of positioning strategies. A few examples are positioning by:
- Product attributes and benefits: Associating your brand/product with certain characteristics or with certain beneficial value
- Product price: Associating your brand/product with competitive pricing
- Product quality: Associating your brand/product with high quality
- Product use and application: Associating your brand/product with a specific use
- Competitors: Making consumers think that your brand/product is better than that of your competitors
A Perceptual Map in Market Positioning
A perceptual map is used to show consumer perception of certain brands. The map allows you to identify how competitors are positioned relative to you and to identify opportunities in the marketplace.
An example of consumers perception of price and quality of brands in the automobile industry are mapped below:
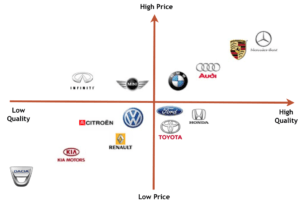
This map is for illustrative educational purposes only.
How to Create an Effective Market Positioning Strategy?
Create a positioning statement that will serve to identify your business and how you want the brand to be perceived by consumers.
For example, the positioning statement of Volvo: “For upscale American families, Volvo is the family automobile that offers maximum safety.”
1. Determine company uniqueness by comparing to competitors
Compare and contrast differences between your company and competitors to identify opportunities. Focus on your strengths and how they can exploit these opportunities.
2. Identify current market position
Identify your existing market position and how the new positioning will be beneficial in setting you apart from competitors.
3. Competitor positioning analysis
Identify the conditions of the marketplace and the amount of influence each competitor can have on each other.
4. Develop a positioning strategy
Through the preceding steps, you should achieve an understanding of what your company is, how your company is different from competitors, the conditions of the marketplace, opportunities in the marketplace, and how your company can position itself.
What is Market Repositioning?
Market repositioning is when a company changes its existing brand or product status in the marketplace. Repositioning is usually done due to declining performance or major shifts in the environment.
Many companies, instead of repositioning, choose to launch a new product or brand because of the high cost and effort required to successfully reposition a brand or product.
Example of Market Repositioning
The example below describes Coca-Cola’s repositioning of Mother Energy Drinks:
The Coca-Cola Company launched Mother Energy Drinks in 2006 into the Australian market. The launch campaign was professionally executed, and Coca-Cola was able to leverage its distribution channels to get the product into major retailers. However, the taste of Mother Energy Drink was subpar and repeat purchases were very low.
Coca-Cola was faced with a decision: to improve and reposition the product or withdraw it and introduce a new brand and product. The company ultimately decided to reposition the product due to already high brand awareness.
The biggest challenge faced by Coca-Cola was to persuade consumers to try the product again. The company changed the packaging, increased the size of the can, and improved the taste of the product. The relaunch of the product featured a new phrase – “New Mother, tastes nothing like the old one.”
Ultimately, Coca-Cola was able to successfully reposition Mother Energy Drinks and the brand today competes with the two leading energy drinks in the market – V and Red Bull.
Other Resources
To learn more and advance your career, see the following free CFI resources:
