Six Sigma
A tool used to identify and reduce errors and increase the efficiency of business processes
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a term used to define various techniques and management tools designed to make business processes more efficient and effective. It provides statistical tools to eliminate defects, identify the cause of the error, and reduce the possibilities of error. Thus, Six Sigma creates an environment of continuous process improvement, enabling businesses to provide better products and services to customers. It was developed by Motorola, Inc. in 1986.

Six Sigma can be applied to any process in any industry to establish a management system for identifying errors and eliminating them. It provides methods to improve the efficiency of business structure and quality of processes, enhancing the profitability of the business.
The term “Six Sigma” is derived from the bell curve in statistics, in which sigma represents the standard deviation from the center. Hence, a process with six sigmas will achieve an extremely low defect rate. The failure of a business process or product is regarded as a defect. When a process produces less than 3.4 defects for one million chances, it is considered efficient.
Summary
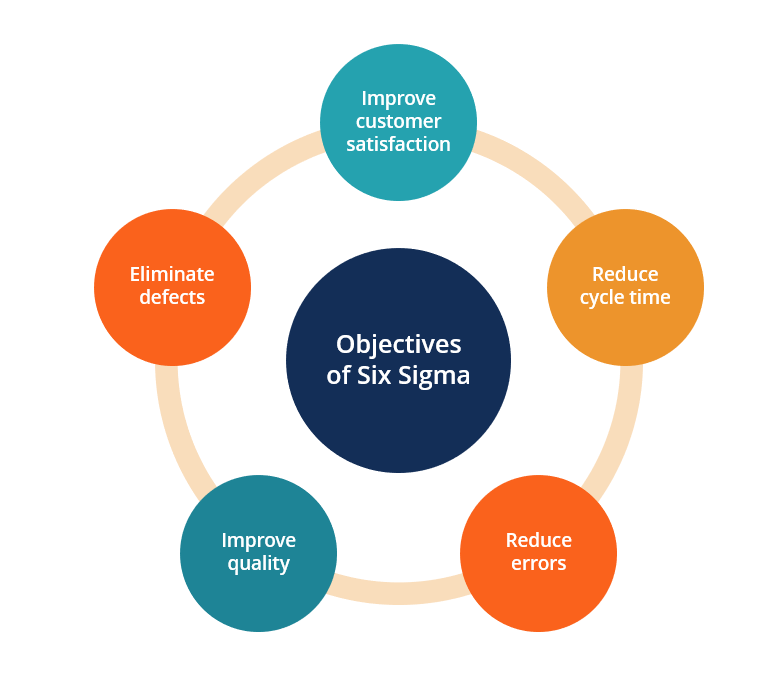
- Six Sigma is used to identify and reduce errors and increase the efficiency of business processes.
- The primary objective of Six Sigma is customer satisfaction, and to achieve the objective, various methods are followed to improve the performance of a product or business process.
- DMAIC and DMADV are the main methodologies of Six Sigma that apply to different business environments.
Six Sigma Principles
There are five main principles of Six Sigma:
1. Customer focus
The main objective is to maximize the benefits for customers. Hence, a business must understand the needs of their customers and the drivers of sales. It requires establishing quality standards according to the market or customer demands.
2. Assess the value chain and find the problem
Outline the steps of a process to find out unwanted areas and gather related data. Define goals for data collection, purposes for data gathering, and expected insights. Verify that the data is assisting in achieving the objectives, whether more information is needed to be collected, or if data cleansing is required. Find out the problem and its root cause.
3. Eliminate defects and outliers
After the identification of the problem, make appropriate modifications in the process to eliminate defects. Eliminate any activity in the given process that does not contribute to the customer value. If the value chain is unable to reveal the problem area, various tools are used to find out the problem areas and outliers. Eliminating the outliers and defects removes the bottlenecks in a given process.
4. Involve stakeholders
A structured process should be adopted where all stakeholders collaborate and contribute to finding solutions to complex issues. The team needs to achieve proficiency in the methodologies and principles applied. Hence, specialized knowledge and training are required to lower project failure risks and ensure optimal performance of the processes.
5. Flexible and responsive system
Whenever an inefficient or faulty process is eliminated, the employee approach and work practices need to be changed. A flexible and responsive environment to the changes in processes can lead to the efficient implementation of the projects.
The departments involved should be capable of adapting easily to the change. Companies that periodically examine the data and make appropriate changes to their processes may achieve a competitive advantage.
Six Sigma Methodology
The following are the two main methodologies of Six Sigma, which are used in different business environments:
DMAIC
DMAIC is a data-driven approach used for optimizing and improving the existing business designs and processes. It is an effective method of controlled change management. The five phases of DMAIC are listed below, and each phase involves tools and tasks to help find the final solution.
- Define the problem and the goals of the project
- Measure the different aspects of the existing process in detail
- Analyze data to find the main flaw in a process
- Improve the given process
- Control the way the process is implemented in the future
DMADV
DMADV focuses on the development of an entirely new process, product, or service. It is used when existing processes, even after improvement, do not satisfy the customer’s needs, and new methods are required to be developed. It comprises five phases:
- Define the purpose of the project, product, or service
- Measure the crucial components of a process and product capabilities
- Analyze data and develop design alternatives, ultimately selecting the best design
- Design the selected best alternative and test the prototype
- Verify the effectiveness of the design through several simulations and a pilot program
Related Readings
CFI is the official provider of the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™ certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst.
To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below: