Straight Line Depreciation
Uniform depreciation of an asset's value
What is Straight Line Depreciation?
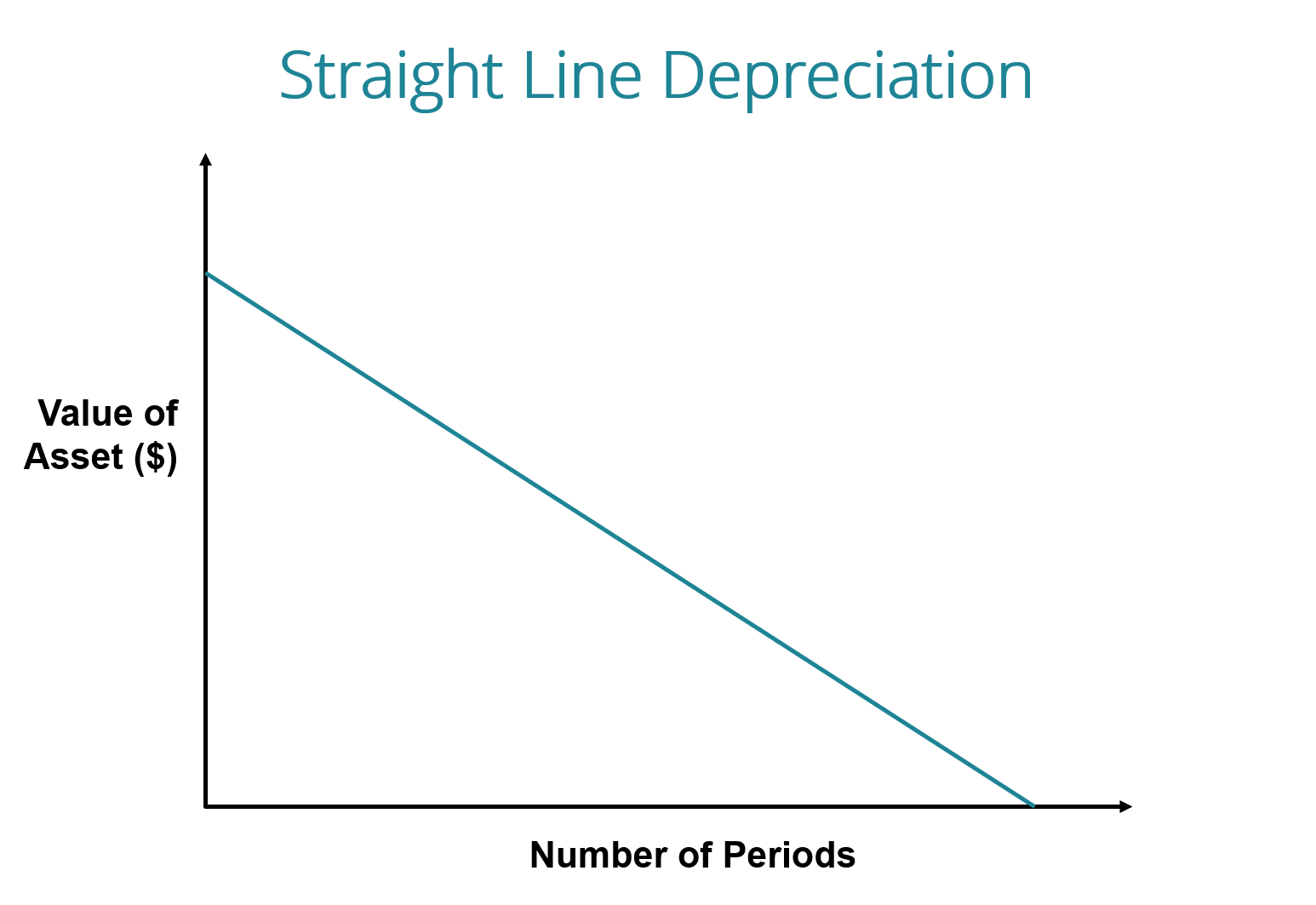
With the straight line depreciation method, the value of an asset is reduced uniformly over each period until it reaches its salvage value. Straight line depreciation is the most commonly used and straightforward depreciation method for allocating the cost of a capital asset. It is calculated by simply dividing the cost of an asset, less its salvage value, by the useful life of the asset.
Image: CFI’s Free Accounting Course.
Straight Line Depreciation Formula
The straight line depreciation formula for an asset is as follows:

Where:
Cost of the asset is the purchase price of the asset
Salvage value is the value of the asset at the end of its useful life
Useful life of asset represents the number of periods/years in which the asset is expected to be used by the company
Additionally, the straight line depreciation rate can be calculated as follows:

How to Calculate Straight Line Depreciation
The straight line calculation steps are:
- Determine the cost of the asset.
- Subtract the estimated salvage value of the asset from the cost of the asset to get the total depreciable amount.
- Determine the useful life of the asset.
- Divide the sum of step (2) by the number arrived at in step (3) to get the annual depreciation amount.
Straight Line Example
Company A purchases a machine for $100,000 with an estimated salvage value of $20,000 and a useful life of 5 years.
The straight line depreciation for the machine would be calculated as follows:
- Cost of the asset: $100,000
- Cost of the asset – Estimated salvage value: $100,000 – $20,000 = $80,000 total depreciable cost
- Useful life of the asset: 5 years
- Divide step (2) by step (3): $80,000 / 5 years = $16,000 annual depreciation amount
Therefore, Company A would depreciate the machine at the amount of $16,000 annually for 5 years.
The depreciation rate can also be calculated if the annual depreciation amount is known. The depreciation rate is the annual depreciation amount / total depreciable cost. In this case, the machine has a straight-line depreciation rate of $16,000 / $80,000 = 20%.
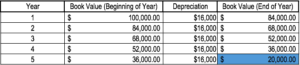
Note how the book value of the machine at the end of year 5 is the same as the salvage value. Over the useful life of an asset, the value of an asset should depreciate to its salvage value.
Download the Straight Line Depreciation Template
Download CFI’s free Excel template now to advance your finance knowledge and perform better financial analysis.
Other Methods of Depreciation
In addition to straight line depreciation, there are also other methods of calculating depreciation of an asset. Different methods of asset depreciation are used to more accurately reflect the depreciation and current value of an asset. A company may elect to use one depreciation method over another in order to gain tax or cash flow advantages.
1. Double-declining balance method
The double-declining balance method is a form of accelerated depreciation. It means that the asset will be depreciated faster than with the straight line method. The double-declining balance method results in higher depreciation expenses in the beginning of an asset’s life and lower depreciation expenses later. This method is used with assets that quickly lose value early in their useful life. A company may also choose to go with this method if it offers them tax or cash flow advantages.
2. Units of production method
The units of production method is based on an asset’s usage, activity, or units of goods produced. Therefore, depreciation would be higher in periods of high usage and lower in periods of low usage. This method can be used to depreciate assets where variation in usage is an important factor, such as cars based on miles driven or photocopiers on copies made.
Video Explanation of How Depreciation Works
Below is a video tutorial explaining how depreciation works and how it impacts a company’s three financial statements.
The Practicality of Straight Line Depreciation
Accountants use the straight line depreciation method because it is the easiest to compute and can be applied to all long-term assets. However, the straight line method does not accurately reflect the difference in usage of an asset and may not be the most appropriate value calculation method for some depreciable assets.
For example, due to rapid technological advancements, a straight line depreciation method may not be suitable for an asset such as a computer. A computer would face larger depreciation expenses in its early useful life and smaller depreciation expenses in the later periods of its useful life, due to the quick obsolescence of older technology. It would be inaccurate to assume a computer would incur the same depreciation expense over its entire useful life.
Related Reading
Thank you for reading this guide to the most common type of depreciation – straight line. To prepare for the FMVA curriculum, these additional CFI resources will be helpful:
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
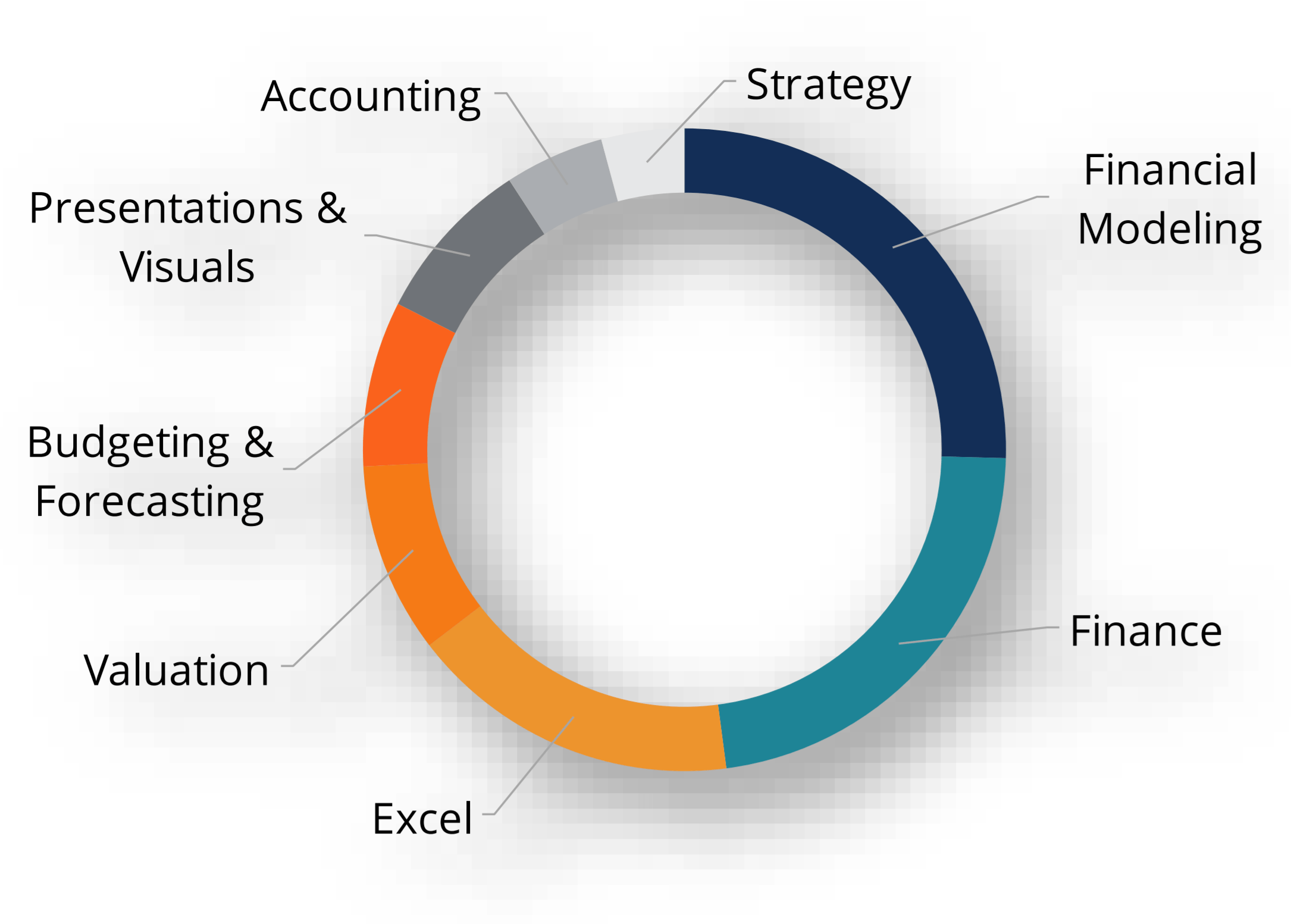
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?