Contribution Margin
A business's sales revenue less its variable costs
What is Contribution Margin?
Contribution margin is a business’s sales revenue less its variable costs. The resulting contribution dollars can be used to cover fixed costs (such as rent), and once those are covered, any excess is considered earnings. Contribution margin (presented as a % or in absolute dollars) can be presented as the total amount, amount for each product line, amount per unit, or as a ratio or percentage of net sales.
Formula for Contribution Margin
In terms of computing the amount:
Contribution Margin = Net Sales Revenue – Variable Costs
OR
Contribution Margin = Fixed Costs + Net Income
To determine the ratio:
Contribution Margin Ratio = (Net Sales Revenue – Variable Costs ) / (Sales Revenue)
Sample Calculation of Contribution Margin
A mobile phone manufacturer has sold 50,000 units of its latest product offering in the first half of the fiscal year. The selling price per unit is $100, incurring variable manufacturing costs of $30 and variable selling/administrative expenses of $10. As a result, the contribution margin for each product sold is $60, or a total for all units of $3 million, with a contribution margin ratio of .60 or 60%.
Key Highlights
- Contribution margin is a business’s sales revenue less its variable costs.
- Contribution margin can be presented as the total amount, amount for each product line, amount per unit, or as a percentage of net sales.
- Variable costs are direct and indirect expenses incurred by a business from producing and selling goods or services. These costs vary depending on the volume of units produced or services rendered.
What are Variable Costs?
Variable costs are direct and indirect expenses incurred by a business from producing and selling goods or services. These costs vary depending on the volume of units produced or services rendered. Variable costs rise as production increases and falls as the volume of output decreases.
Also, it is important to note that a high proportion of variable costs relative to fixed costs, typically means that a business can operate with a relatively low contribution margin. In contrast, high fixed costs relative to variable costs tend to require a business to generate a high contribution margin in order to sustain successful operations.
Examples of variable costs are:
- Direct materials – Raw materials that are primarily needed in producing goods
- Production supplies – Items such as oil and lubricants used to maintain machines
- Per unit labor – Amount paid to workers per unit completed
- Billable wages – Amount paid to workers as per their billed worked hours
- Commissions – Amount paid to salespersons for every unit sold
- Freight in/out costs – Shipping or transportation expense which is only incurred when there are goods for delivery ordered by customers
- Variable utilities – Electricity and water used to produce volumes of goods and services
What are Fixed Costs?
Fixed costs are expenses incurred that do not fluctuate when there are changes in the production volume or services produced. These are costs that are independent of the business operations and which cannot be avoided. In determining the price and level of production, fixed costs are used in break-even analysis to ensure profitability.
Examples of fixed costs are:
- Depreciation – Allocation of the costs for property, plant, and equipment, which is spread throughout its useful life
- Interest expense – Interest rate on a loan that needs to be paid on a periodic basis
- Insurance – Premiums paid under an insurance contract
- Rent – Periodic expense for leasing a property
- Property taxes – Tax charged by the government based on the assessed value of the property
- Salaries – Fixed amount paid to workers or employees for their services, regardless of hours worked
- Fixed utilities – Cost of electricity, water, and gas generally used in office administration
How Important is Contribution Margin in Business?
When a company is deciding on the price of selling a product, contribution margin is frequently used as a reference for analysis. Fixed costs are usually large – therefore, the contribution margin must be high to cover the costs of operating a business.
A low or negative contribution margin indicates a product line or business may not be that profitable, so it is not wise to continue making the product at its current sales price level unless it is a very high volume product.
It is important to assess the contribution margin for break-even or target income analysis. The target number of units that need to be sold in order for the business to break even is determined by dividing the fixed costs by the contribution margin per unit.
To resolve bottlenecks, contribution margin can be used to decide which products offered by the business are more profitable and, therefore, more advantageous to produce, given limited resources. Preference is given to products that provide a high contribution margin.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Contribution Margin. In order to help you become a world-class financial analyst and advance your career to your fullest potential, these additional resources will be very helpful:
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
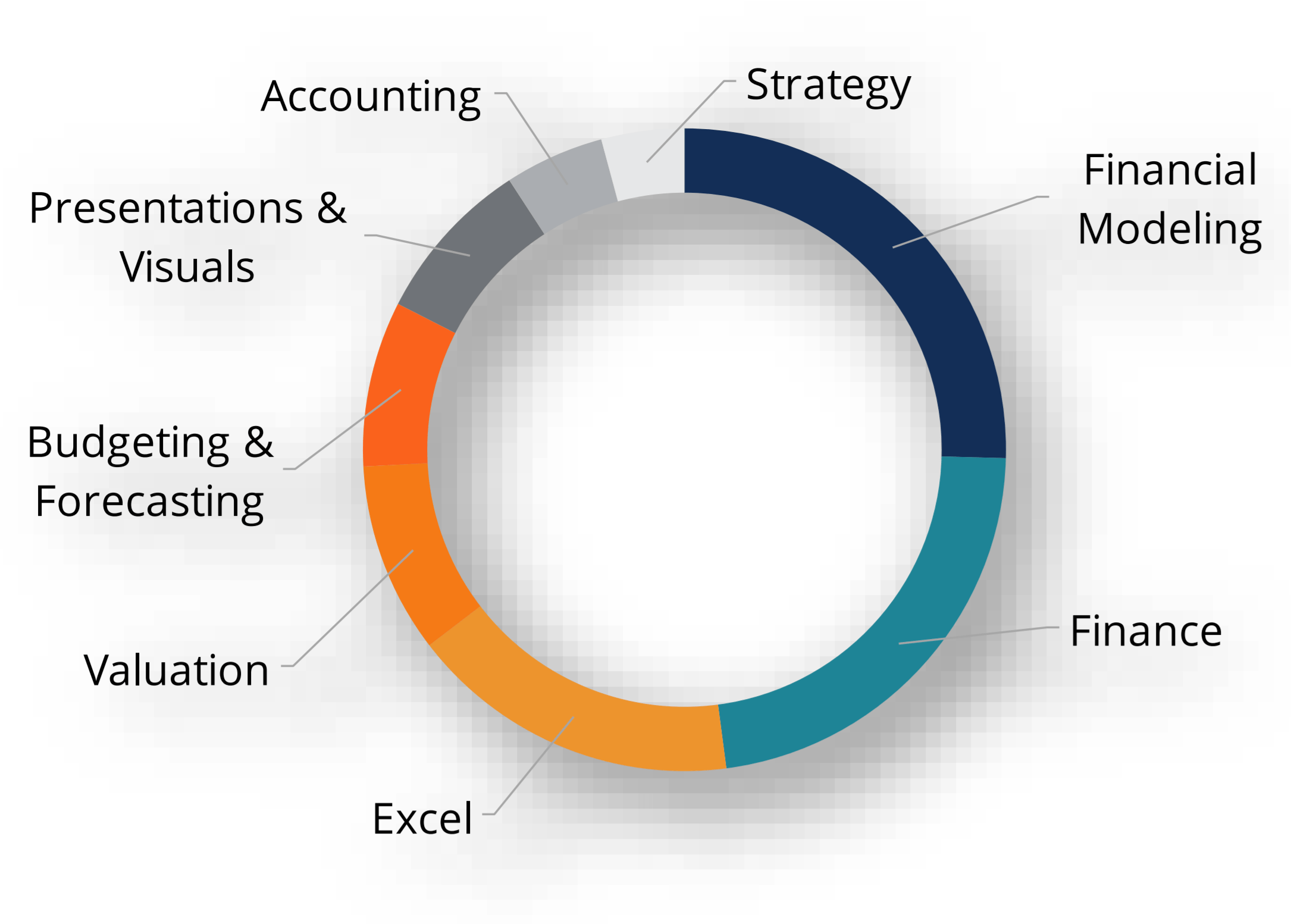
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?