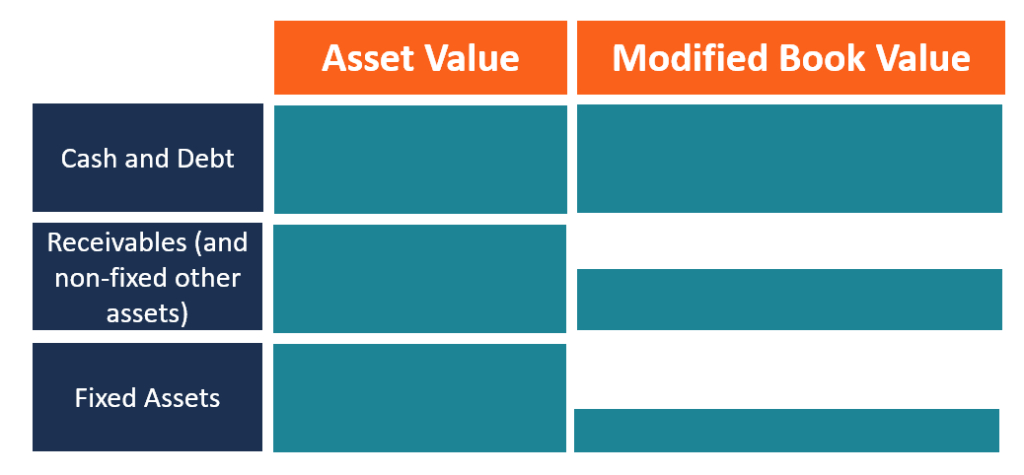
Modified Book Value
Adjusting the net worth of assets and liabilities to obtain their fair market value
What is Modified Book Value?
Modified book value is one of the several valuation methods used by analysts and investors to assign a value to a company. The modified book value method works by adjusting the net worth of a company’s assets and liabilities to obtain their fair market value. For example, the market value of a real estate may be different from the historical value and may be determined by conducting an appraisal of the asset to obtain its fair market value.
How Modified Book Value Works
The modified book value method is commonly used when evaluating distressed companies that are anticipating bankruptcy. The method adjusts the value of tangible assets line by line to arrive at a bottom-line price. Currents assets like cash on hand and short-term debt are already captured at their fair market value, and they are recorded as they are.
However, an asset like accounts receivables will be adjusted depending on their age. Receivables that are due in six months are more likely to be adjusted downwards since there is a likelihood of some debtors defaulting on their obligations. It may not be the case for short receivables such as 30 days and 45 days receivables that are still too young to make an allowance for bad debts. Another current asset that requires to be adjusted is inventory, which is modified according to the method of accounting for inventory like LIFO and FIFO.
Fixed assets such as land, buildings, and property, plant and equipment (PPE) require large adjustments since their valuations are different compared to current assets. For example, the value of land recorded on the balance sheet is the historical cost, and it needs to be adjusted to reflect the current fair market value of the asset. Ideally, the fair market value of the land will be higher than the historical cost, since land appreciates in value over a period of time.
However, for assets such PP&E and motor vehicles, the fair market value of the assets will be lower than the historical cost, since these types of assets are subject to depreciation, which decreases the value of the asset. Other types of assets that require to be adjusted to their fair market value include intangible assets, contingent liabilities, and deferred tax assets. After getting the modified book values of all assets and liabilities, you should deduct the liabilities from the assets to obtain the market value of the company.
How to Compute a Modified Book Value
The following is the basic process that you can follow when computing the modified book value of a firm:
- The first step is to access the company’s annual report, either on the company’s website or by requesting a hard copy from the investor relations department. Next, go to the balance sheet and identify the assets and liabilities that need to be adjusted to their fair market value.
- The next step is to calculate the book value by subtracting liabilities from the total assets. If the total assets are $500,000 and the liabilities are $100,000, the book value, in this case, is $400,000.
- Calculate the market value of the assets. The book value of assets like cash in hand and short-term debts does not need to be adjusted since they are calculated on the balance sheet date. Conduct an appraisal of the assets to get their current value and add the difference to the book value calculated in step 2 above.
- Go to the Off-Balance Sheet Items to get the assets that have been excluded from the balance sheet. Add these assets to the value obtained in step 3 to get the adjusted book value.
More Resources
CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following resources will be helpful:
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
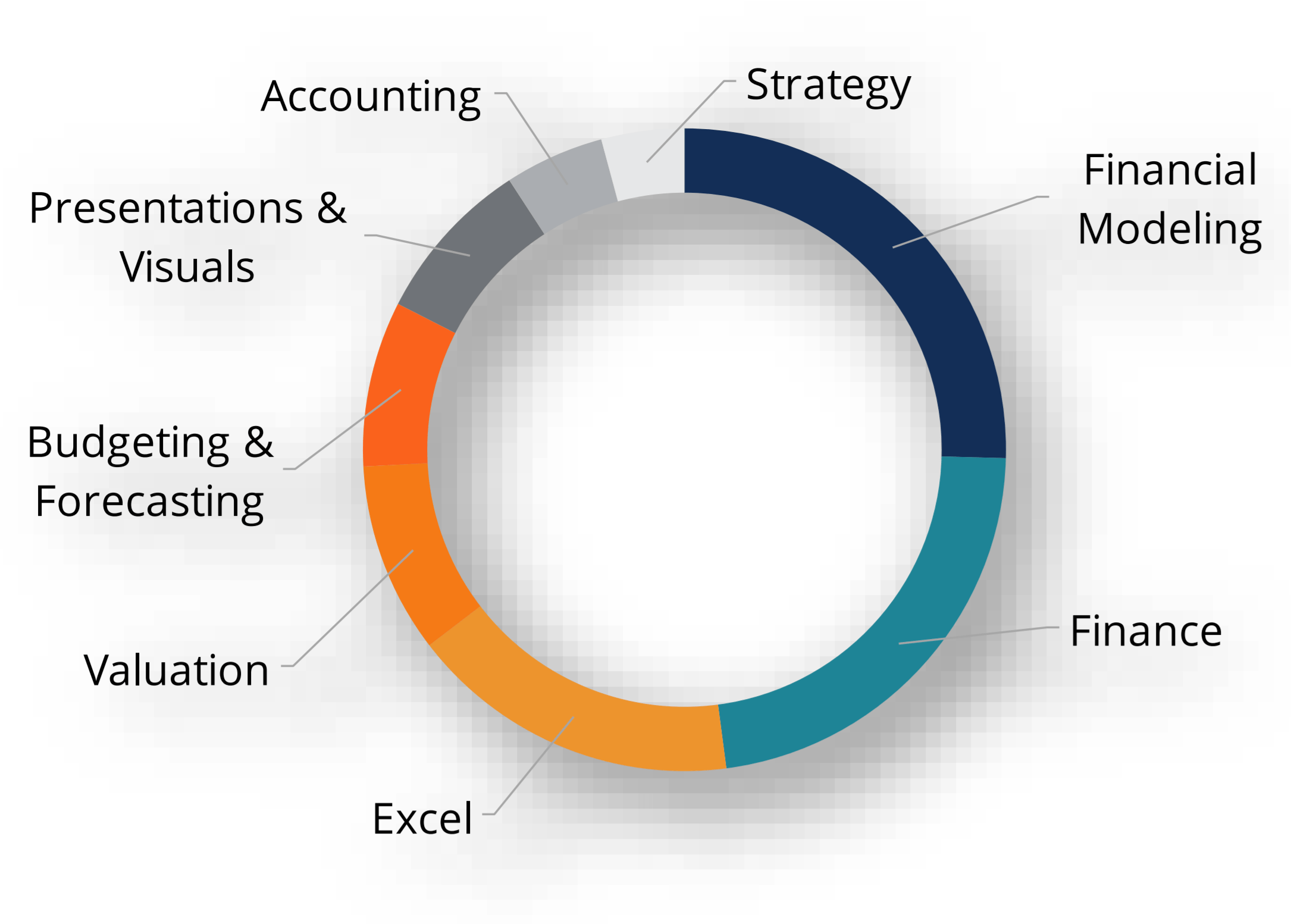
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?
Accounting Crash Courses
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s online accounting classes.
These courses will give you the confidence to perform world-class financial analyst work. Start now!
Boost your confidence and master accounting skills effortlessly with CFI’s expert-led courses! Choose CFI for unparalleled industry expertise and hands-on learning that prepares you for real-world success.