Asset Purchase vs Stock Purchase
Pros and cons of each deal type
Asset Purchase vs Stock Purchase
When buying or selling a business, the owners and investors have a choice: the transaction can be a purchase and sale of assets or a purchase and sale of common stock. The buyer of the assets or stock (the “Acquirer”) and the seller of the business (the “Target”) can have various reasons for preferring one type of sale over the other. This guide examines the Asset Purchase vs Stock Purchase decision in detail.
Acquisitions can be structured either as an asset transaction or as a stock transaction. Where an asset transaction is favored, a variety of issues must be considered, as the transaction is actually the sum of the sales of each of the individual assets and an assumption of agreed-upon liabilities.
Where the transaction is structured as a stock acquisition, by its very nature, the acquisition results in a transfer of the ownership of the business entity itself, but the entity continues to own the same assets and have the same liabilities.

Asset Purchase
In making an asset sale, the seller remains as the legal owner of the entity. At the same time, the buyer purchases individual assets of the company, such as equipment, licenses, goodwill, customer lists, and inventory.
Asset sales generally do not include purchasing the target’s cash, and the seller typically retains its long-term debt obligations. Such a sale is characterized as cash-free and debt-free.
Normalized net working capital is typically included in an asset purchase agreement. Net working capital is comprised of items such as accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable.
Asset Purchase vs Stock Purchase: Asset Advantages
Here are several advantages of an asset purchase transaction:
- A major tax advantage is that the buyer can “step up” the basis of many assets over their current tax values and obtain tax deductions for depreciation and/or amortization.
- With an asset transaction, goodwill, which is the amount paid for a company over and above the value of its tangible assets, can be amortized on a straight-line basis over 15 years for tax purposes. In a stock deal, with the acquirer buying shares of the target, goodwill cannot be deducted until the stock is later sold by the buyer.
- The buyer can dictate what, if any, liabilities it is going to assume in the transaction. This limits the buyer’s exposure to liabilities that are large, unknown, or not stated by the seller. The buyer can also dictate which assets it is not going to purchase. If, for example, the buyer determines that the seller has a lot of accounts receivable that are probably uncollectable, then they can simply elect not to purchase the Target’s AR (accounts receivable).
- Because the exposure to unknown liabilities is limited, the buyer typically needs to expend less time and money, and fewer resources, on conducting due diligence.
- Minority shareholders who don’t want to sell their shares can effectively be forced to accept the terms of an asset sale. Unlike the case with a stock purchase, minority shareholders do not ordinarily have to be taken into account in regard to an asset purchase.
- The buyer can select which employees they want to retain (and which they do not) without impacting their unemployment rates.
Asset Purchase vs Stock Purchase: Asset Disadvantages
Here are several disadvantages of an asset purchase as compared to a stock purchase:
- Contracts – especially with customers and suppliers – may need to be renegotiated and/or renovated by the new owner
- The tax cost to the seller is typically higher, so the seller may insist on receiving a higher purchase price.
- Assignable contract rights may be limited.
- Assets may need to be retitled.
- Employment agreements with key employees may need to be renegotiated.
- The seller still needs to liquidate any assets not purchased, pay any liabilities that have not been assumed, and take care of any leases that need to be terminated.
Stock Purchase
A stock purchase is simpler in concept than an asset purchase. Therefore, in most instances, it’s just basically an easier, less complex transaction.
The Acquirer buys the stock of the target and takes the target as it finds it, in regard to both assets and liabilities. Most contracts the target has – such as leases and permits – transfer automatically to the new owner. For all these reasons, it’s often more straightforward to go with a stock purchase rather than an asset purchase.
Advantages of a Stock Purchase
The following are several advantages of doing a stock purchase:
- The acquirer doesn’t have to bother with costly re-valuations and retitles of individual assets.
- Buyers can typically assume non-assignable licenses and permits without having to obtain specific consent.
- Buyers may also be able to avoid paying transfer taxes.
- More simple and commonly used than an asset acquisition. Hedge funds are known for commonly conducting M&A transactions in the form of a simple stock purchase.
Disadvantages of a Stock Purchase
Here are some of the disadvantages of a stock purchase:
- The main disadvantage is that an acquirer receives neither the “step-up” tax benefit nor the advantage of handpicking assets and liabilities.
- All assets and liabilities transfer at carrying value.
- The only way to get rid of unwanted liabilities is to create separate agreements wherein the target takes them back.
- Applicable securities laws, of course, have to be dealt with, and this can complicate the process, especially when the target has a lot of shareholders. Additionally, some shareholders may not wish to sell their stocks, and this can drag out the process and increase the cost of acquisition.
- Goodwill is not tax-deductible when it exists in the form of a share price premium.
Choosing the form of an acquisition transaction can have significant tax and other business-related consequences for both buyer and seller. Both parties should explore and consider the benefits and consequences of each type of transaction, with the help of professional financial advisors, to determine whether an asset purchase or stock purchase transaction best suits their wants and needs.
Additional Resources
This guide to evaluating an Asset Purchase vs Stock Purchase has highlighted the main pros and cons of each transaction type. To keep learning about other forms of M&A transactions, please see the following additional CFI resources:
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
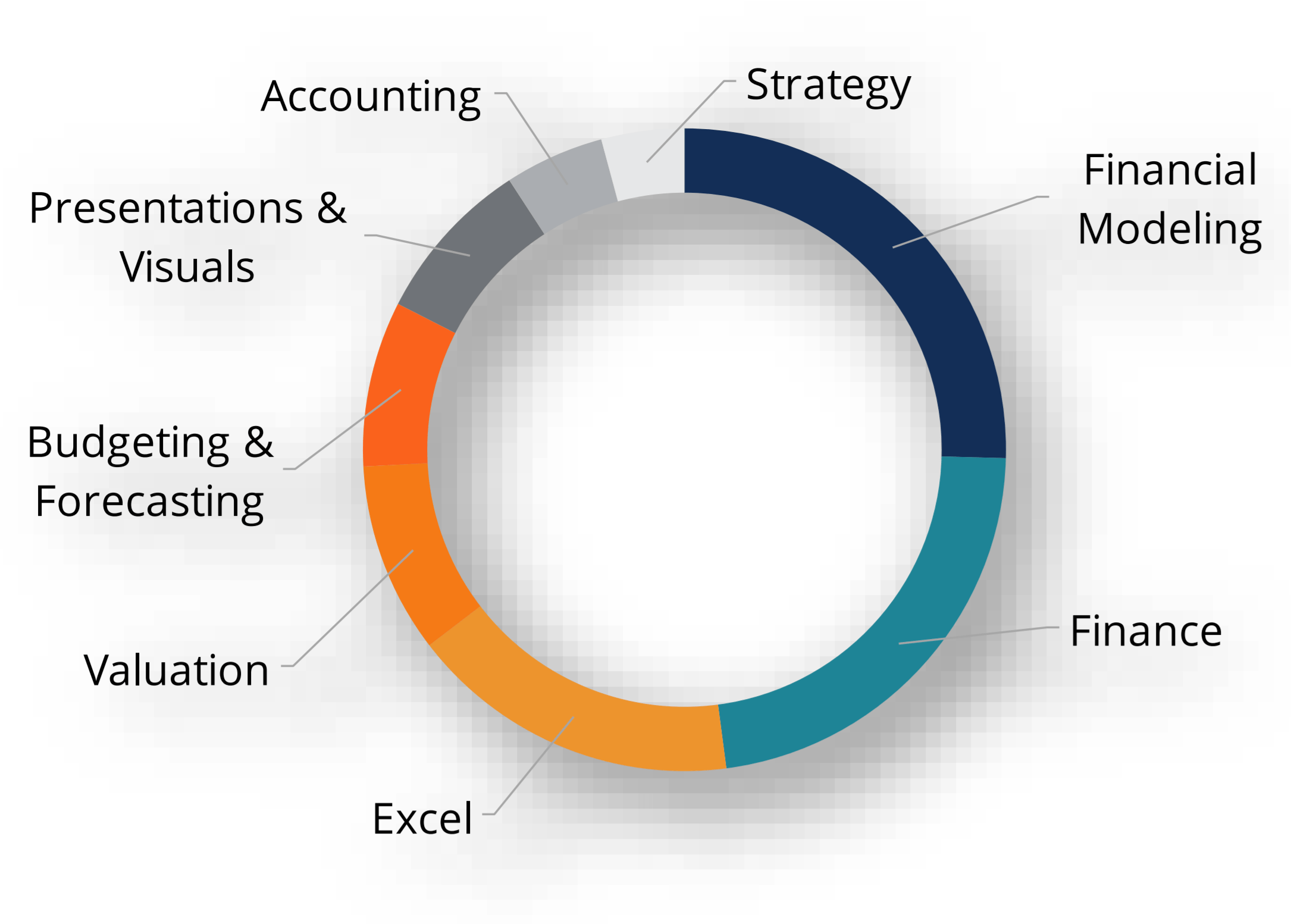
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?