CAC LTV Ratio
Customer Acquisition Cost and Customer Lifetime Value
What is the LTV/CAC Ratio?
LTV stands for “lifetime value” per customer and CAC stands for “customer acquisition cost.” The LTV/CAC ratio compares the value of a customer over their lifetime to the cost of acquiring them.
This eCommerce metric compares the value of a new customer over its lifetime relative to the cost of acquiring that customer.
If the LTV/CAC ratio is less than 1.0, the company is destroying value, and if the ratio is greater than 1.0, it may be creating value, but more analysis is required. Generally speaking, a ratio greater than 3.0 is considered “good,” but that’s not necessarily the case.
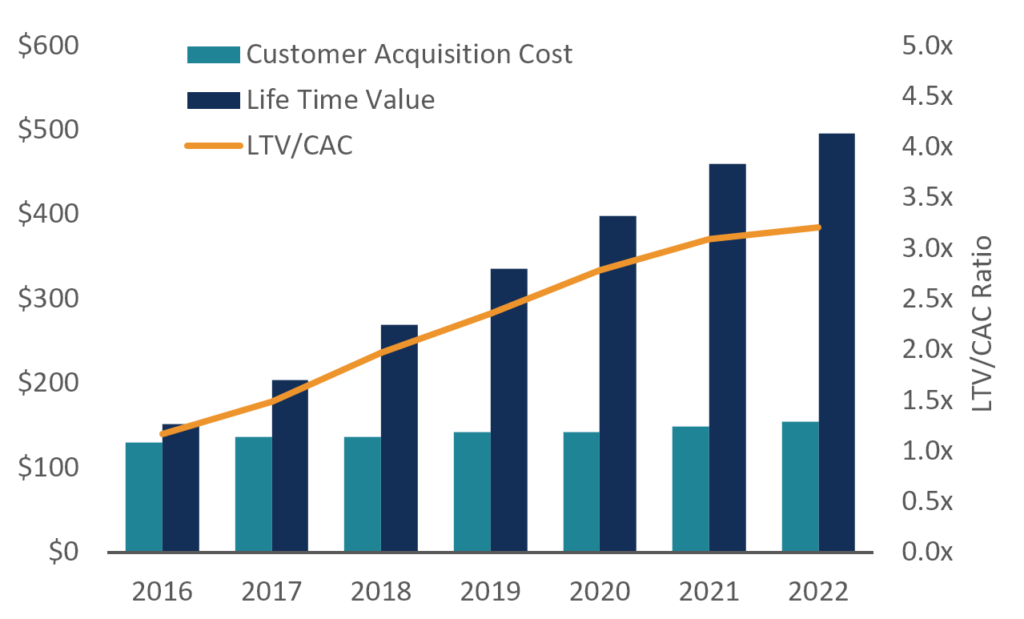 Chart: CFI eCommerce Financial Modeling Course
Chart: CFI eCommerce Financial Modeling Course
LTV/CAC Ratio Formula
Below is the lifetime value to customer acquisition cost formula:
LTV/CAC Ratio = [(Revenue Per Customer – Direct Expenses Per Customer) / (1 – Customer Retention Rate)] / (Direct Marketing Spending / No. of Customers Acquired)
Example Calculation
An eCommerce company spends $10,000 on a Google AdWords campaign and acquires 1,000 new customers. The average revenue per customer is $50, and the direct cost of filling each order is $30. The company retains 75% of its customers per year.
Customer contribution margin = $50 – $30 = $20
LTV = $20 / (1 – 75%) = $80
CAC = $10,000 / 1,000 = $10
LTV/CAC ratio = $80 / $10 = 8.0x
In this case, the ratio is quite high and the company is profitably acquiring customers – assuming there are not a huge amount of fixed costs in the business.
Download the Free Template
Download CFI’s Excel template to advance your finance knowledge and perform better financial analysis.
Challenges With the LTV/CAC Ratio
Contribution margin is not necessarily a good indication of economic benefit. Companies may have high fixed costs that need to be factored in.
- Retention rates (or churn rate) change with time and are not constant.
- Customer acquisition costs also change with time and are not constant.
To learn more about CAC and LTV, check out our online course on eCommerce Financial Modeling. This course will show you step-by-step how to model the economics of a marketing campaign for an eCommerce business.
More Learning
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to CAC LTV Ratio. To learn more about other types of return on investment, you may want to check out:
- Return on Ad Spend
- Return on Assets
- Profit Margin
- LTV CAC Ratio Template
- See all valuation resources
To find out more about finance careers, check out the CFI interactive Career Map.
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
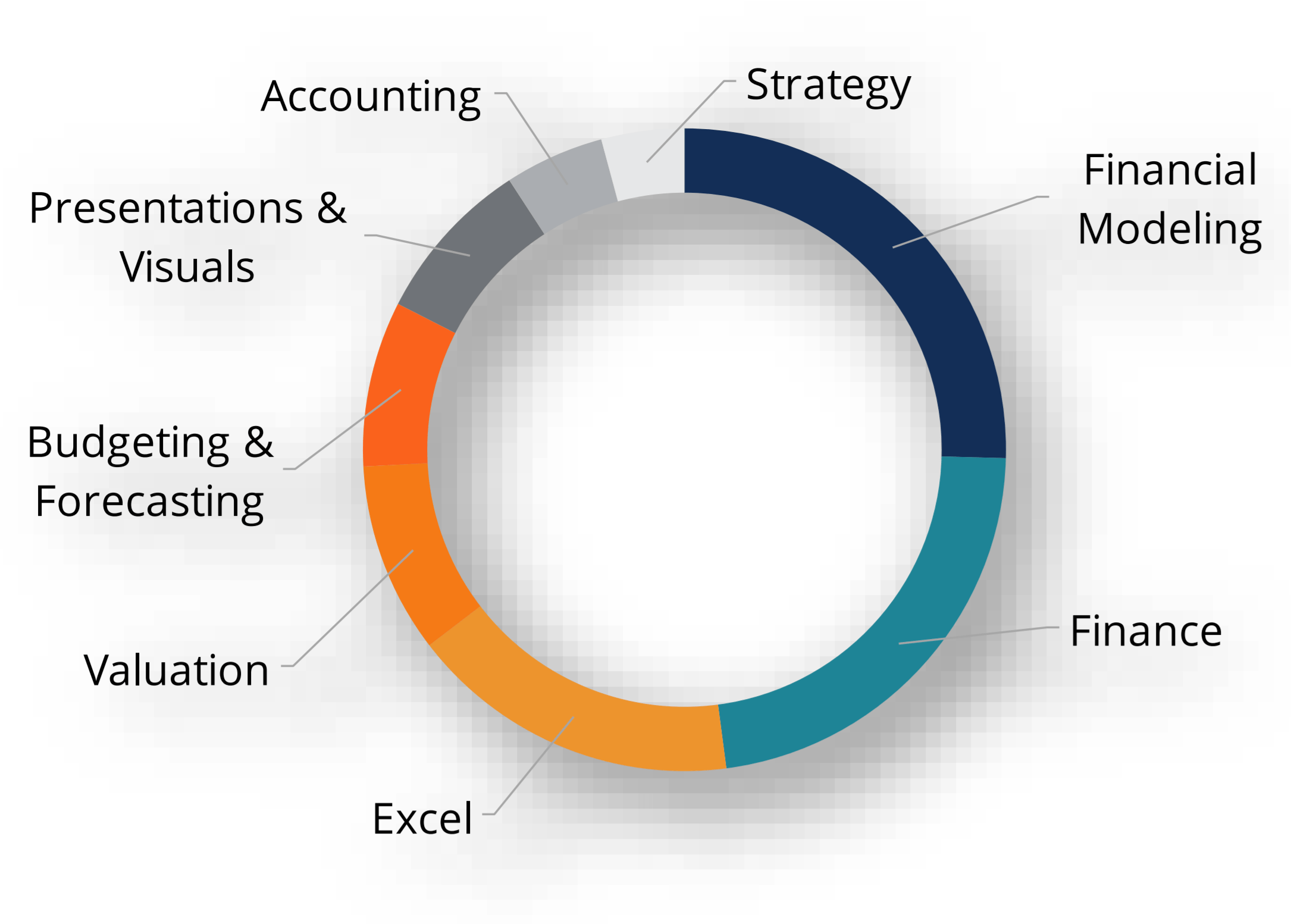
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?
Accounting Crash Courses
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s online accounting classes.
These courses will give you the confidence to perform world-class financial analyst work. Start now!
Boost your confidence and master accounting skills effortlessly with CFI’s expert-led courses! Choose CFI for unparalleled industry expertise and hands-on learning that prepares you for real-world success.