Notes Payable
Written agreements to repay the lender a certain amount of cash
What are Notes Payable?
Notes payable are written agreements (promissory notes) in which one party agrees to pay the other party a certain amount of cash. Alternatively put, a note payable is a loan between two parties.
A note payable contains the following information:
- The amount to be paid
- The interest rate applied to the loan
- The maturity date
- Name of the maker of the note (payer)
- Name of the payee
- The signature of the person who issued the note with the date signed.

Notes Payable on a Balance Sheet
Notes payable appear as liabilities on a balance sheet. Additionally, they are classified as current liabilities when the amounts are due within a year. When a note’s maturity is more than one year in the future, it is classified with long-term liabilities.
An example of different accounts on a balance sheet:
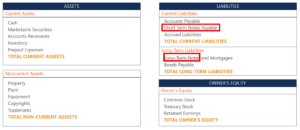
Notice how notes payable can be short-term or long-term in nature.
Example
John borrowed $100,000 from Michelle on January 1, 2022. John signs the note and agrees to pay Michelle $100,000 six months later (January 1 through June 30). Additionally, John also agrees to pay Michelle a 15% interest rate every 2 months.
The journal entries would be as follows:

The Difference Between Accounts Payable and Notes Payable
The concept of accounts payable and notes payable are often mixed up. A definition of both of these terms along with their respective attributes are detailed below:
Accounts Payable
Accounts payable is an obligation that a business owes to creditors for buying goods or services. Accounts payable do not involve a promissory note, usually do not carry interest, and are a short-term liability (usually paid within a month).
Notes Payable
These are written agreements in which the borrower obtains a specific amount of money from the lender and promises to pay back the amount owed, with interest, over or within a specified time period. It is a formal and written agreement, typically bears interest, and can be a short-term or long-term liability, depending on the note’s maturity time frame.
Creating an Enforceable Promissory Note
To create an enforceable promissory note, the following elements must be included:
- The loan amount
- The repayment dates
- The interest rate
- Default terms
- The names of both the lender and the borrower
- Mailing address where each payment is mailed to
- The borrower should print, sign, and date the promissory note
Notes Receivable
Both the items of Notes Payable and Notes Receivable can be found on the Balance Sheet of a business. While Notes Payable is a liability, Notes Receivable is an asset. Notes Receivable record the value of promissory notes that a business owns, and for that reason, they are recorded as an asset. NP is a liability which records the value of promissory notes that a business will have to pay. This is analogous to accounts receivable vs. accounts payable.
Additional Resources
CFI’s mission is to help anyone in the world become a confident financial analyst through the CFI Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® credential program. To continue learning and advancing your career, these additional CFI resources will be helpful:
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
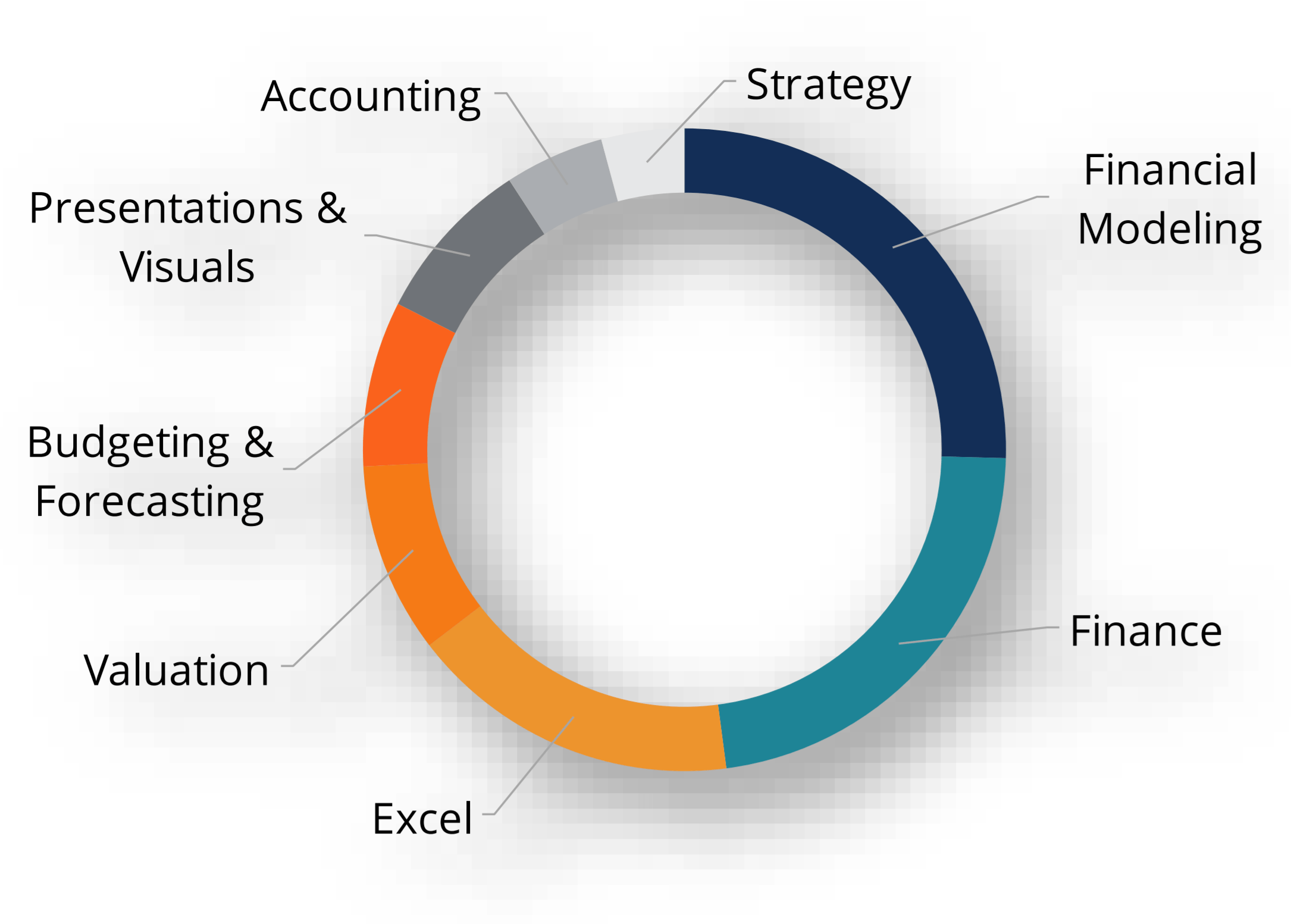
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?
Accounting Crash Courses
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s online accounting classes.
These courses will give you the confidence to perform world-class financial analyst work. Start now!
Boost your confidence and master accounting skills effortlessly with CFI’s expert-led courses! Choose CFI for unparalleled industry expertise and hands-on learning that prepares you for real-world success.