XNPV Function in Excel
How and why to use the function in financial analysis
Why Use the XNPV Function in Excel?
The XNPV Function[1] in Excel uses specific dates that correspond to each cash flow being discounted in the series, whereas the regular NPV function automatically assumes all the time periods are equal. For this reason, the XNPV function is far more precise and should be used instead of the regular NPV function.
For additional learning, read CFI’s list of top Excel formulas.
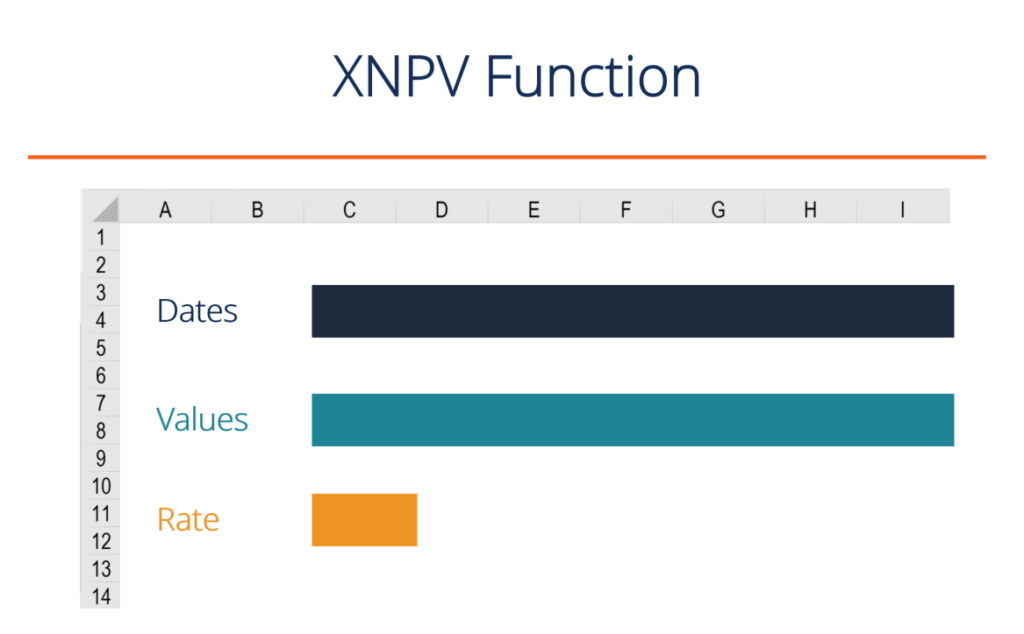
What is the XNPV function formula?
The XNPV formula in Excel requires the user to select a discount rate, a series of cash flows, and a series of corresponding dates for each cash flow.
The Excel formula for XNPV is:
=XNPV(Rate, Cash Flows, Dates of Cash Flow)
The XNPV function uses the following three components:
- Rate – The discount rate to be used over the length of the period (see hurdle rate and WACC articles to learn about what rate to use).
- Values (Cash Flows) – This is an array of numeric values that represent the payments and income where:
- Negative values are treated as outgoing payments (negative cash flow).
- Positive values are treated as income (positive cash flow).
- Dates (of Cash Flows) – An array of dates corresponding to an array of payments. The date array should be of the same length as the values array.
The XNPV function uses the following equation to calculate the Net Present Value of an investment:
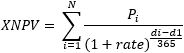
Where:
- di = the i‘th payment date
- d1 = the 0’th payment date
- Pi = the i‘th payment
Please see the example below for a detailed breakdown of how to use XNPV in Excel.
Example of the XNPV Function in Excel
Below is a screenshot of an Example of the XNPV function being used in Excel to calculate the Net Present Value of a series of cash flows based on specific dates.
Key assumptions in the XNPV example:
- The discount rate is 10%
- The start date is June 30, 2018 (date we are discounting the cash flows back to)
- Cash flows are received on the exact date they correspond to
- The time between the start date and the first cash flow is only 6 months

Based on the above, the XNPV formula produces a value of $772,830.7 while the regular NPV formula produces a value of $670,316.4.
The reason for this difference is that XNPV recognizes that the time period between the start date and first cash flow is only 6 months, while the NPV function treats it as a full-time period.
Download the XNPV template
If you’d like to incorporate this function in your own financial modeling and valuation work, please feel free to download CFI’s XNPV function template and use it as you see fit.
It may be a good idea to experiment with changing the dates around and seeing the impact on valuation, or the relative difference between XNPV vs NPV in the Excel model.
XNPV vs NPV implications
The results of the comparisons of XNPV vs NPV formulas produces an interesting result and some very important implications for a financial analyst. Imagine if the analyst were valuing a security and didn’t use the proper time periods that XNPV takes into account. They would be undervaluing the security by a meaningful amount!
Use in financial modeling
XNPV is used routinely in financial modeling as a means of calculating the net present value (NPV) of an investment opportunity.
For all types of financial models, XNPV and XIRR are highly recommended over their date-less counterparts NPV and IRR.
While the added precision will have you feeling more confident about your analysis, the only downside is that you have to pay careful attention to the dates in your spreadsheet and make sure the start date always reflects what it should.
For a transaction such as a Leveraged Buyout (LBO) or an acquisition, it’s important to be precise about the closing date of the deal. For example, you may be building the model now, but the closing date will likely be several months in the future.
To see the function in action, check out CFI’s financial modeling courses!
Things to remember about the XNPV function
Below is a helpful list of points to remember:
- Numbers in dates are truncated to integers.
- XNPV doesn’t discount the initial cash flow (it brings all cash flows back to the date of the first cash flow). Subsequent payments are discounted based on a 365-day year.
- #NUM! error – Occurs when either:
- The values and dates arrays are of different lengths; or
- Any of the other dates are earlier than the start date.
- #VALUE! error – Occurs when either:
- The values or rates arguments are non-numeric; or
- The given dates are not recognized by Excel as valid dates.
XIRR vs IRR
To learn more about XIRR vs IRR we have created a similar guide, which we highly recommend you check out to further solidify the concept. For the same reasons as noted above in this guide, it’s equally important to use specific dates when calculating the internal rate of return on an investment.
If you’re considering a career in investment banking or private equity, then you will be required to use these functions extensively.
More Resources from CFI
We hope this has been a helpful guide to help you understand how to incorporate the important XNPV Excel function in your financial modeling.
To keep expanding your knowledge base and advancing your career as a Professional Financial Modeler we believe these additional CFI resources will be helpful as well:
- Hurdle Rate Overview
- WACC Formula
- Guide to Financial Modeling
- Advanced Excel Formulas
- See all Excel resources
Article Sources
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
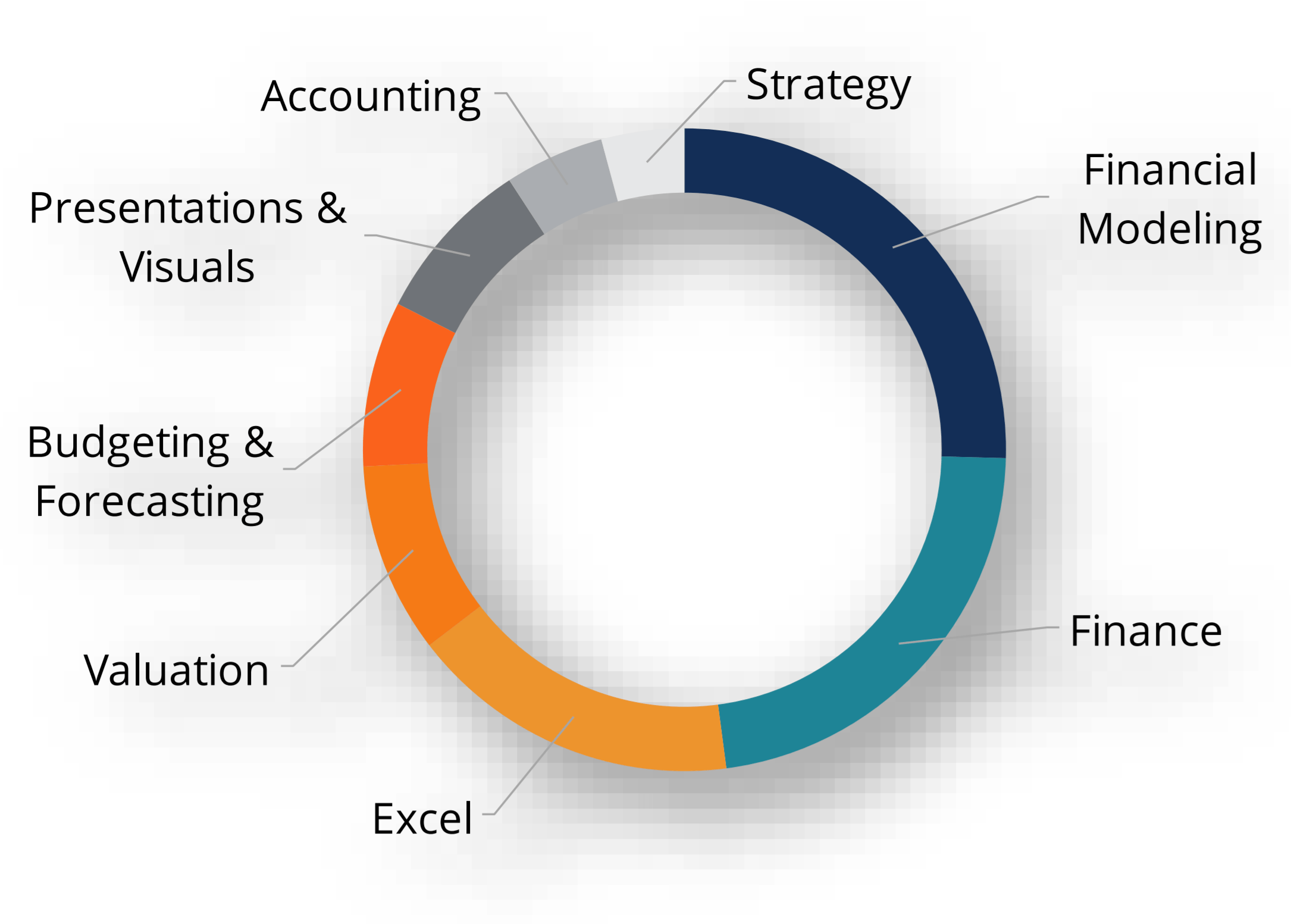
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?
Excel Tutorial
To master the art of Excel, check out CFI’s Excel Crash Course, which teaches you how to become an Excel power user. Learn the most important formulas, functions, and shortcuts to become confident in your financial analysis.
Launch CFI’s Excel Crash Course now to take your career to the next level and move up the ladder!