Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing.

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics, geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory. For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research, products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
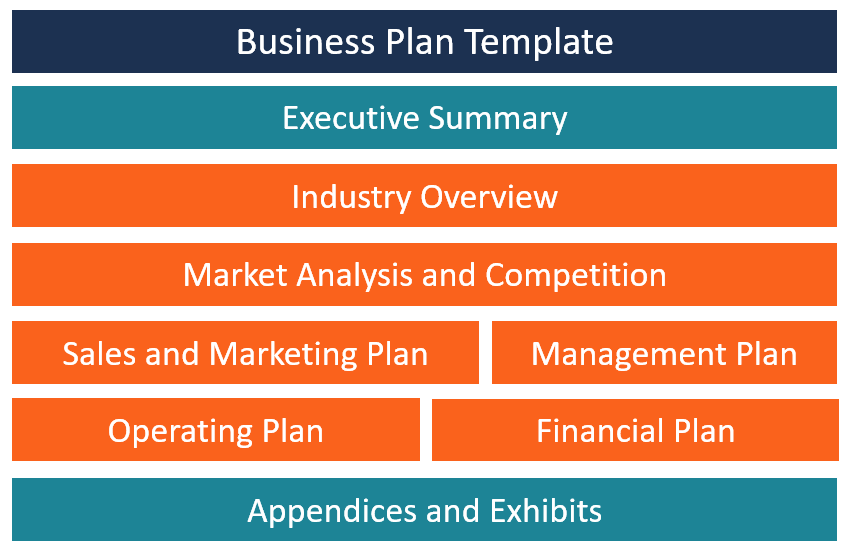
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in