- What is a Distribution Channel?
- Role of Distribution Channels in Business
- Types of Distribution Channels
- Understanding Key Players and Levels of Distribution Channels
- Business Distribution Channels: Examples
- 1. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) E-Commerce
- 2. Retail Partnerships
- 3. Wholesale Distribution
- 4. Online Marketplaces (Third-Party E-Commerce)
- 5. Franchise Model
- How Do Distribution Channels Benefit Businesses?
- Market Expansion
- Efficient Delivery
- Cost Optimization
- Targeted Reach
- Market Insights
- Customer Satisfaction
- The Internet as the Modern-Day Distribution Channel
- What to Consider When Developing a Channel and Distribution Strategy
- Expand Your Knowledge and Propel Your Career
Distribution Channels: The Efficient Flow of Goods and Services
The strategic flow of goods from producers and manufacturers to consumers
The best products only succeed when they reach their customers efficiently. Smart distribution strategy shapes both business operations and market performance, giving you the tools to drive company growth. Whether you’re analyzing operations, managing teams, or building business knowledge, your expertise in distribution channel strategy directly impacts market success.
At CFI, we teach you how to build effective channel and distribution approaches that top companies rely on. You’ll master strategies that connect products to customers and deliver measurable business results. Our programs equip you with practical skills that strengthen your decision-making at every career stage, from emerging professionals to experienced leaders. So, what are distribution channels, and how do they work? Let’s break it all down.
What is a Distribution Channel?
Distribution channels create connections between manufacturers and customers. Every step— from the factory floor through warehouses and stores to your final purchase—forms part of this network. These same channels show how revenue flows back through the system, connecting your transactions to company earnings. Understanding these dynamics helps you see how successful companies optimize their operations for maximum market impact.

Companies must carefully select their distribution channel strategy based on their products, market characteristics, and customer needs. Whether they’re leveraging direct channels to sell directly to consumers or building multiple distribution channels to expand their reach, their approach needs to align with their broader business objectives.
For manufacturers, finding the right mix of distribution channels makes products readily available to customers. The diversity and scope of your business will determine which channels generate the best sales and provide the easiest customer access.
Key Highlights
- A channel of distribution moves products from creation to customer, tracking how goods flow from manufacturer to final purchase.
- Most channels rely on intermediaries — wholesalers, retailers, or brokers — that connect makers to buyers. These middlemen can be individuals or companies.
- Your channel structure can be direct (straight to the customer) or indirect (using intermediaries). Indirect channels vary in complexity, from simple one-step paths to networks with multiple layers.
Role of Distribution Channels in Business
Every company must establish strong paths to market — a web of relationships that brings products from factory to consumer. These partners influence your product pricing and market positioning across every industry, from major wholesalers to individual brokers.
Distribution channels power your business operations through several essential functions:
- Connect Production to Profit: A strong channel of distribution in business lets you focus on making great products while partners handle logistics, storage, and delivery. This specialization improves efficiency across your entire supply chain, from manufacturing to final sale
- Reach More Customers: The right mix of retailers, online marketplaces, and specialty shops expands your market presence. Using multiple intermediaries opens access to established customer bases and helps you scale without building everything from scratch
- Build Customer Loyalty: Reliable distribution makes products available where and when customers expect them. This consistency in stock levels and delivery times builds trust and encourages repeat purchases
- Control Costs and Stock: Well-designed networks minimize storage costs while maintaining optimal inventory levels. Each step between production and purchase adds expense, so your channels should maximize efficiency while reducing unnecessary touchpoints
Your distribution strategy should streamline the journey from production to purchase. This means choosing partners who operate at full capacity while maintaining competitive rates. Every decision about your distribution network affects both operational costs and market performance.
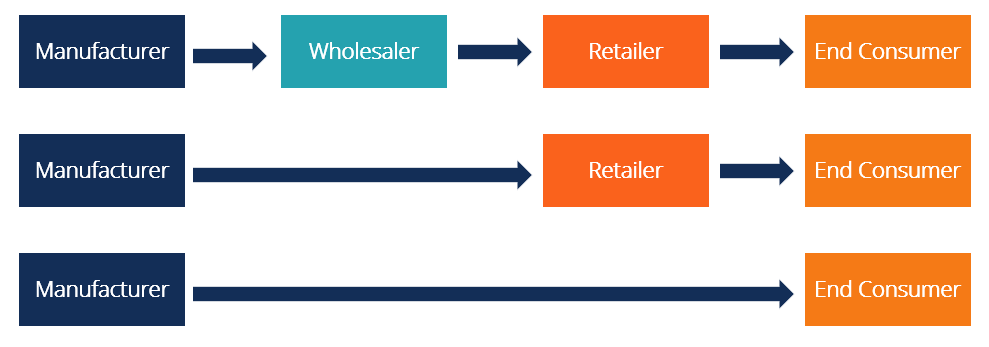
Types of Distribution Channels
The structure of a distribution channel depends on the number of intermediaries involved in moving a product from production to purchase. Businesses use direct, indirect, and hybrid distribution channels to deliver products and services. Each of these channels of distribution offers distinct advantages depending on your goals and market strategy.
1. Direct distribution channels
A direct distribution channel involves selling products or services directly to the end customer without using intermediaries. This approach gives you full control over pricing, branding, and customer relationships, creating a more personalized buying experience.
Common examples include:
- Online channels: Selling directly through a company’s website eliminates third-party retailers and provides full control over pricing and customer interactions.
- Direct sales through company-owned retail stores: Operating physical locations strengthens brand identity and allows businesses to manage sales and services directly.
- Direct contact with customers: Using independent representatives creates a personal connection with customers and expands outreach.
Direct distribution works best when you want to establish a direct relationship with your customers, tailor the buying experience, and increase sales without third-party influence.
2. Indirect distribution channels
An indirect distribution channel relies on intermediaries such as wholesalers, retailers, and brokers to deliver products to consumers. This method helps businesses expand their reach, streamline logistics, and access established sales networks.
Common examples include:
- Wholesalers supply their products to retailers, who then sell to consumers.
- Retail partnerships with supermarkets and department stores to increase availability.
- Exclusive distribution agreements that control where and how products are sold.
Indirect distribution channels allow you to scale efficiently by leveraging existing distribution networks and industry relationships.
3. Hybrid distribution channels
A hybrid channel strategy combines direct and indirect channels to maximize your market reach and enhance flexibility. This approach lets you engage customers across multiple touchpoints while optimizing distribution.
Common examples include:
- Omnichannel strategies where you sell through your company’s website, physical stores, and third-party marketplaces.
- Partnerships with online retailers while maintaining a direct-to-consumer model.
By blending different distribution methods, you can generate demand, strengthen brand presence, and adapt to shifting consumer preferences.
Understanding Key Players and Levels of Distribution Channels
Choosing the right distribution strategy requires a clear understanding of the different distribution levels and the players involved. Each distribution channel follows a distinct structure, influencing how products move from production to purchase.
Five key players shape a distribution channel strategy:
- Producer/Manufacturer: Creates the product or service
- Agent: Connects manufacturers with wholesalers or retailers, typically earning a commission
- Wholesaler: Buys in bulk and distributes to retailers
- Retailer: Sells directly to consumers through stores or online platforms
- End Consumer: The final purchaser and user of the product
By understanding these key players and their roles, businesses can identify the most efficient and effective product distribution model. Let’s explore the four main levels of distribution channels and how they impact product reach, cost, and market accessibility.
1. Level-0 Channel
A Level-0 distribution channel, or direct selling, involves no intermediaries. The product moves straight from the manufacturer to the end consumer. You’ll often see this model in Software as a Service (SaaS), where businesses sell subscriptions directly to customers.
2. Level-1 Channel
A Level-1 channel introduces retail partners between the manufacturer and the consumer. Common in the business strategy of large retail brands, this structure allows you to expand your reach while maintaining control over branding and pricing. Many large retail brands use this approach to ensure broad product availability.

3. Level-2 Channel
A Level-2 channel includes both wholesalers and retailers, creating a more structured supply chain. This model is widely used for consumer goods, where wholesalers purchase in bulk, break shipments into smaller quantities, and distribute them to retailers. The two-level channel is ideal for affordable, durable goods with broad market appeal.

4. Level-3 Channel
A Level-3 channel adds an agent or broker as an additional intermediary. Unlike the two-level model, products move from the manufacturer to an agent before reaching wholesalers and retailers.
Agents help manage sales, coordinate logistics, and ensure products reach the right markets. This model is especially useful when you need to expand into multiple regions or international markets where longer distribution channels are required to manage a complex supply chain for longer distribution channels.
Agents typically receive a commission and oversee distribution in assigned territories. A three-level channel is ideal for selling high-demand products across a wide geographic market.

Business Distribution Channels: Examples
Selecting the right distribution channel is essential for maximizing reach, efficiency, and profitability. The best approach depends on your target audience, product type, and operational capacity. Different industries use a variety of distribution strategies, each with distinct advantages and challenges. Understanding these models can help you refine your own approach and align it with your business goals.
1. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) E-Commerce
How It Works: You sell directly to customers through websites or online stores, eliminating intermediaries like wholesalers or retailers.
Benefits:
- Maintain full control over pricing, branding, and customer relationships.
- Increase profit margins by removing third-party costs.
- Gain insights into customer preferences that help refine marketing and product strategies and boost customer satisfaction.
Challenges:
- Requires investment in digital marketing and logistics.
- Customer acquisition costs can be high without strong brand recognition.
Example: Warby Parker disrupted the eyewear industry by selling glasses online, bypassing traditional retailers, offering home try-ons, and eliminating the need for in-store visits.
2. Retail Partnerships
How It Works: Your products are distributed through established retail partners, such as supermarkets, department stores, or specialty shops.
Benefits:
- Increases brand visibility and credibility through trusted retail networks.
- Leverages the retailer’s existing customer base.
- Reduces the need to manage logistics and fulfillment.
Challenges:
- Retailers may demand high-profit margins, reducing manufacturer earnings.
- Limited control over how products are marketed and displayed.
Example: Coca-Cola distributes its beverages globally through convenience stores, grocery chains, and vending machines, ensuring intensive distribution and mass availability.
3. Wholesale Distribution
How It Works: You sell in bulk to wholesale distributors, who then supply retailers or businesses.
Benefits:
- Reduces storage and distribution costs.
- Provides efficient delivery to retailers who cannot purchase directly from producers.
- Expands market reach without handling individual sales transactions.
Challenges:
- Profit margins may be lower due to wholesaler markups.
- Less direct interaction with end consumers, limiting brand control.
Example: Tech companies sell devices in bulk to wholesalers, who distribute them to electronic retailers worldwide.
4. Online Marketplaces (Third-Party E-Commerce)
How It Works: You list and sell products on platforms like Amazon or eBay, which handle sales, logistics, marketing, and payment processing.
Benefits:
- Access to a large, built-in customer base.
- Reduces operational burden by outsourcing payment processing and logistics.
- Supports multiple distribution channels, increasing visibility.
Challenges:
- Platform fees and commissions can reduce profitability.
- Competition is high, making brand differentiation essential.
Example: Many businesses, from small startups to global brands, leverage Amazon’s fulfillment services to distribute their products worldwide.
5. Franchise Model
How It Works: You license your brand, business model, and operational systems to independent franchisees who manage local stores.
Benefits:
- Expands business reach with lower capital investment.
- Franchisees handle daily operations, reducing corporate workload.
- Helps standardize customer experience across multiple locations.
Challenges:
- Requires strong oversight to maintain brand consistency.
- Success depends on franchisees upholding quality and service standards.
Example: McDonald’s uses a franchise model to expand globally while allowing local operators to run individual locations.
When learning about business distribution channels, examples like these can help you identify the best strategies to optimize reach, improve efficiency, and support long-term growth.
How Do Distribution Channels Benefit Businesses?
A well-designed distribution channel strategy helps streamline operations, increase revenue, and improve customer satisfaction. Effective distribution channels ensure that products and services reach customers effectively, whether you sell directly or through intermediaries.
Market Expansion
Effective distribution channels help you reach new markets through direct sales, wholesale partnerships, or entry into online channels. Multiple distribution channels allow you to tap into diverse customer segments, increase brand visibility, and scale operations globally.
Efficient Delivery
A streamlined distribution network ensures that products reach customers quickly and reliably. Optimizing your supply chain through wholesale distributors, retail partners, or direct customer interaction can reduce delays and improve fulfillment efficiency.
Cost Optimization
Choosing the right strategy helps you lower operational costs by reducing inventory management expenses and inefficiencies in longer distribution channels, improving overall logistics. You can cut costs by using direct channels to eliminate retailer markups or outsourcing distribution to channel partners.
Targeted Reach
Different distribution channels allow you to tailor your sales approach to specific audience needs. Selective distribution through high-end retailers preserves exclusivity for luxury products, while intensive distribution maximizes accessibility for mass-market products.
Market Insights
Using both direct and indirect channels gives you valuable data on customer preferences, demand trends, and overall business performance. Engaging with consumers through online channels or direct-to-consumer (DTC) models provides insights to inform marketing and product development.
Customer Satisfaction
A well-structured distribution channel ensures that customers can easily access products through their preferred purchasing method, in-store, online, or mobile app. By optimizing channel strategies, you can improve the shopping experience, strengthen brand loyalty, and drive repeat purchases.
The Internet as the Modern-Day Distribution Channel
The internet has reshaped how you can distribute products and services, making it a vital part of modern business strategies. Digital channels provide direct access to customers, streamlined sales processes, and global scalability, allowing you to optimize distribution more efficiently.
Types of online distribution channels include:
- E-commerce marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon, AliExpress, eBay, and Alibaba allow businesses to access vast customer bases without the overhead of physical retail locations.
- Social commerce: Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok enable you to sell directly within social media, combining engagement with seamless transactions.
- Subscription-based services: Streaming services and SaaS companies use recurring subscriptions to deliver content or software without relying on physical distribution.
By incorporating online channels into your distribution strategy, you can expand your market reach, reduce costs, and improve customer accessibility. As digital commerce continues to evolve, optimizing your online presence and digital sales channels will help you stay competitive in an increasingly connected marketplace.
What to Consider When Developing a Channel and Distribution Strategy
Selecting the right distribution strategy requires balancing market reach, cost efficiency, and operational feasibility. The channels you choose influence how customers access your products, how quickly orders are fulfilled, and how well your brand is positioned in the marketplace. A thoughtful approach ensures that your distribution model supports business growth and customer expectations.
Market Characteristics
Your distribution strategy should reflect how, where, and when your target audience prefers to make purchases. Factors such as customer location, buying habits, and technological adoption play a major role in determining whether direct, indirect, or hybrid distribution is the best fit.
For instance, businesses selling specialized equipment may benefit from direct sales, while mass-market products typically require wholesale or retail partnerships to ensure broad accessibility.
Product Characteristics
The type of product you sell influences the most effective distribution channel definition for your business. Perishable goods, luxury items, and high-value industrial equipment often require selective or direct distribution to maintain quality and exclusivity.
In contrast, low-cost consumer goods benefit from intensive distribution, ensuring availability across multiple retail and online channels. Packaging, storage requirements, and product lifecycle also impact how goods are moved through the supply chain.
Competitor Characteristics
Understanding how competitors structure their distribution channels can help you identify opportunities to differentiate. If traditional retail models dominate your industry, shifting to direct-to-consumer sales, subscription services, or e-commerce marketplaces may provide an edge. Analyzing pricing strategies, geographic reach, and distribution efficiency can also reveal gaps in the market where an alternative channel approach could be more effective.
Company Characteristics
Your internal capabilities influence which distribution model is most practical and scalable. Factors such as logistics infrastructure, financial resources, and brand positioning determine whether you should manage distribution internally or partner with third-party providers.
Some businesses benefit from in-house fulfillment and direct customer engagement, while others achieve better efficiency by outsourcing to wholesalers, distributors, or third-party logistics (3PL) providers. The right approach should balance cost, efficiency, and long-term growth potential.
A clear distribution channel definition helps you establish the most effective way to get products into customers’ hands while optimizing costs and efficiency. By evaluating market conditions, product requirements, competitor strategies, and internal capabilities, you can develop a distribution model that maximizes reach, improves logistics, and supports sustainable business growth.
Expand Your Knowledge and Propel Your Career
Knowing how to move products efficiently is a game-changer in business. Mastering distribution channels helps you drive growth, cut costs, and strengthen market positioning. To stay ahead, you need practical skills that deliver real results.
At CFI, we provide expert-led courses and industry-recognized certifications that help you build real-world expertise. Whether you want to refine your strategy, advance your career, or improve a company’s distribution efficiency, our programs give you the tools to succeed.
Take the next step in your professional growth:
- Earn a CFI Certification: Stand out with credentials like FMVA®, CMSA®, and BIDA®. Explore Certifications →
- Build Your Skills with CFI Courses: Learn at your own pace with courses designed for finance professionals. Browse Courses →
- Access Free Finance Resources: Stay ahead with expert insights, templates, and guides. Get Free Resources →
Take charge of your career today and gain the expertise to make a lasting impact in the industry!
Additional Resources
Thank you for exploring CFI’s guide to distribution channels. Keep building your expertise with these additional resources:
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in





