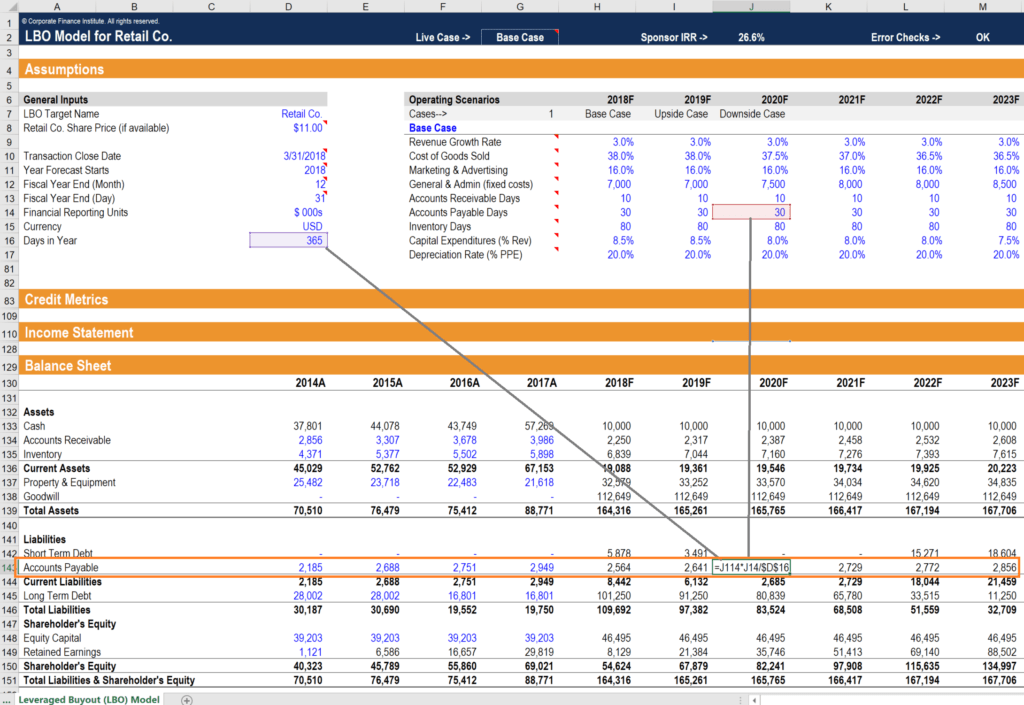
0 search results for ‘’
People also search for:
excel
power bi
esg
accounting
balance sheet
fmva
real estate
Explore Our Certifications
Resources
Popular Courses
Recent Searches

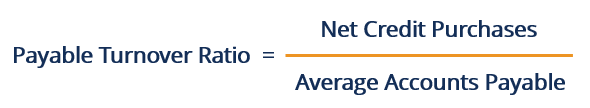
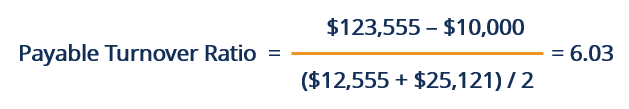
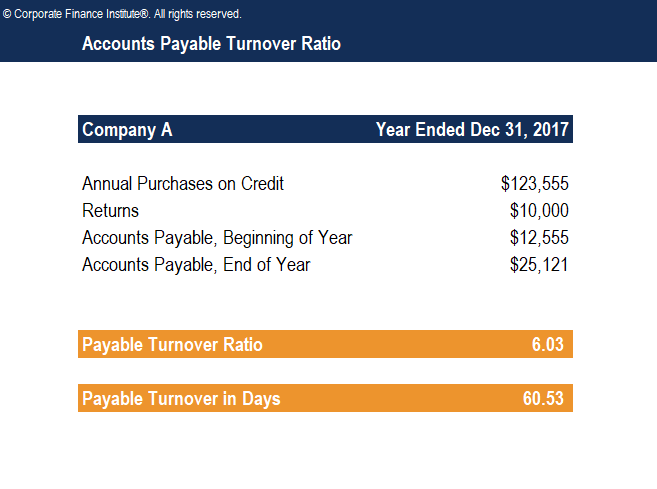 Download CFI’s Free Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio Template
Download CFI’s Free Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio Template